The worst nuclear disaster the world has ever known, began with a trial run of an experimental cooling protocol on April 26, 1986. A power surge occurred in reactor #4 at the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant, near the town of Pripyat in the Ukraine (then part of the USSR.) An emergency shut down was attempted, but the situation was already out of control. Another power surge – stronger than the first – ruptured the containment vessel through a series of explosions that launched radioactive fuel and core materials into the atmosphere. When the reactor’s graphite moderator was exposed to open air, it ignited in a fire that sent a plume of smoke, ripe with radioactive material into the atmosphere.
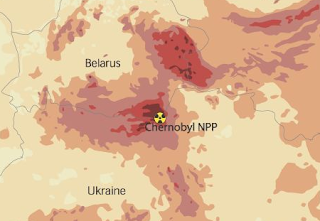 |
| Map of Chernobyl’s radioactive fallout |
The plume drifted over parts of the former Soviet Union and Europe releasing into the open more radioactive material than the atomic bomb dropped of Hiroshima during World War II. The most effected regions include Belarus, Ukraine and what is now Russia – though radioactive material was detected at elevated levels throughout Europe.
The disaster killed 31 people who either worked at the reactor or were part of the emergency response crew, but the number of people who have been killed as a result of subsequent radiation exposure vary from the World Health Organization’s estimated 4,000 to the Greenpeace estimate of 200,000 or more.
The Soviet Union tried hard to downplay the April 26th fire and explosion back in 1986, but two days later on April 28th workers at the Forsmark Nuclear Power Plant in Sweden 680 miles from Chernobyl detected radioactive particles on their clothes. Sweden’s search for the source of the radioactivity (after it was determined that there was no problem at their plant) led to the conclusion that a serious incident had occurred in the western part of the Soviet Union. Chernobyl become the center of world wide attention.
On the 25th anniversary of the Chernobyl disaster, society is still dealing with the legacy of fear, misinformation, and health effects left by the destroyed power plant. Chernobyl was ranked as a level 7 disaster on the International Nuclear Event Scale (INES,) which is the highest possible ranking. The world is still reeling from March’s Fukushima nuclear disaster in Japan, the only other INES level 7 disaster in history. But Fuskushima is not Chernobyl. Fukushima has not caused the level of death and destruction as Chernobyl – and the plants were of completely different designs.
The nuclear reactors at Chernobyl were made based on a now defunct Soviet design, which had known cooling problems. The plant’s workers were testing a new cooling protocol because it was known that in the event of a power outage the system in place (back up generators, etc.) would not have been able to cool the reactors quickly enough. There has been much speculation about who is to blame for the Chernobyl incident – if it was the reactor design or if it was human error.
 |
| Chernobyl as it is today |
The first reports out of Chernobyl blamed the workers – reporting that they didn’t have adequate training and experience, that they were operating the plant with key safety systems (like the Emergency Core Cooling System) turned off, and that they knowingly ignored regulations. However, over time the role of these accusations has been downplayed, while flaws in the design of the control rods (part of the cooling system) and the reactors ability to deal with the build up of steam has been blamed for the bulk of the incident.
The initial clean up of Chernobyl was done by “liquidators” who moved the majority of debris into the damaged reactor, which was covered in sand, lead and boric acid dropped from helicopters. A concrete enclosure was built around the damaged reactor – a task that exposed the construction workers to significant amounts of radiation.
In February I did a post on What We Don’t Know about Chernobyl – namely that the site of the damaged reactor has been without a proper containment vessel all these years. The concrete sarcophagus originally erected around the destroyed reactor is still in place, and there are cracks in it. The money was never raised to build a more permanent enclosure.
The Fukushima disaster has brought Chernobyl back into the headlines, and today on its 25th anniversary we have to stop and ask ourselves how our understanding of nuclear power has been influenced and shaped by that April day back in 1986. In the wake of a nuclear disaster many people question whether the science is really safe, but I think the question we should really be asking is whether the science, in human hands, is really safe. It isn’t an issue of nuclear power – it is an issue of what happens when people try to harness nuclear power.